What are cardiovascular diseases?
Cardiovascular diseases are blood and heart disorders that may lead to heart attacks and strokes. Often these events are caused by blockages that prevent blood from flowing to the heart and brain. Usually, the blockages are caused by fatty deposits on the inner walls of the blood vessels. Strokes may also occur if there is bleeding from blood clots or a blood vessel in the brain.
The Dangers
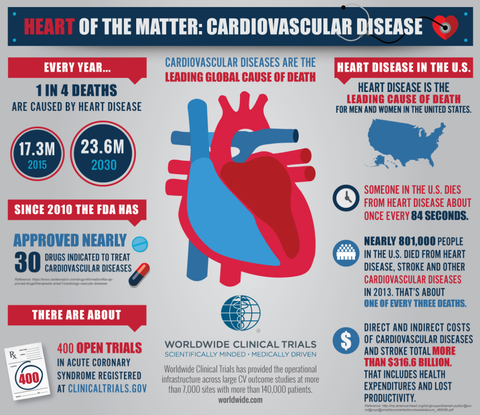
Cardiovascular diseases are the #1 cause of death and disability in the world.
Countries that have low to middle income are especially vulnerable to cardiovascular diseases. 3 out of 4 deaths from cardiovascular disease occur in these countries. Detection of the diseases and getting treatment takes longer in these areas and there is also less access to quality health care services.

Symptoms
Often there are no symptoms to indicate a person suffers from cardiovascular disease – until a heart attack or stroke hits. In the event of a heart attack or stroke medical care should be sought immediately.
Indications of a stroke include:
- Numbness in the face, arm, or leg (especially only on one side of the body)
- Intense headache
- Confusion while attempting to communicate
- Fainting/unconsciousness
- Difficulty seeing through one or both eyes
- Lack of balance and coordination – feeling dizzy
Warning signs of a heart attack include:
- Feeling light-headed or faint
- Pain in the chest, arms, left shoulder, elbows, jaw, or back
- Difficulty breathing
- Becoming pale
- Experiencing a cold sweat
- Feeling nauseous and vomiting

Treatment
Treatment of cardiovascular diseases may include counseling, surgical procedures, and medicine.
Some people are at a higher risk for cardiovascular disease than others. Those experiencing hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidaemia are in the high-risk category. There is medicine to help treat these conditions and proper health care can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Prevention
After an initial stroke or heart attack, often doctors will prescribe medications to help prevent another occurrence.
Most cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by practicing good health habits such as:
- Avoid the use of tobacco and alcohol
- Avoid obesity
- Exercise
- Eat a healthy diet - limit salt and eat fruits and vegetables
- Take multi-vitamins - Many people do not get enough of the recommended nutrients from their diet and supplements can help make up for that gap. Many studies suggest links between taking vitamin and mineral supplements and the prevention of heart disease. For optimum health, look for a high-quality multi-vitamin as supplements are not all created equal.
Summary
Cardiovascular disease is the #1 cause of death in the world. There are many things that can be done to treat and prevent these diseases. Becoming aware of the dangers and taking steps towards a healthier lifestyle can offer the very best protection.
ENP is dedicated to giving back. Our primary focus for 2020-21 is the American Heart Association's Go Red campaign. Learn more about what we're doing to support the American Heart Association.
Sources:
“8 Heart Health Supplements to Take – and One to Avoid.” PeaceHealth, 16 Apr. 2020, www.peacehealth.org/healthy-you/8-heart-health-supplements-take-and-one-avoid.
“Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs).” World Health Organization, World Health Organization, 17 May 2017, www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds).
“Infographic: Every Heart Counts.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 26 Sept. 2018, www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/infographics/every-heart-counts.html.
“What Is Cardiovascular Disease?” Www.heart.org, www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease.